BMI, or Body Mass Index, has long been used as a standard metric to assess an individual’s weight and categorize them into different health classifications. However, recent research and scientific evidence have unveiled numerous inaccuracies associated with BMI, rendering it an obsolete and unreliable tool. In our previous blog we discussed Excessive Exercise Exposed: 5 Red Flags You Shouldn’t Ignore. In this blog post, we will explore the blunders of BMI and provide three key reasons why it’s time to abandon its use in favor of more comprehensive and personalized approaches to health assessment.
Why BMI is Inaccurate?
 BMI is a numerical value derived from an individual’s weight and height.
BMI is a numerical value derived from an individual’s weight and height.
The formula used to calculate BMI is weight in kilograms divided by the square of height in meters.
Based on this calculation, individuals are categorized into different BMI ranges, including underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obese.
While BMI is widely used and easily accessible, it fails to capture crucial aspects of an individual’s body composition and overall health.
The Blunders of BMI
1. Limitations of BMI as a measurement tool
 BMI, or Body Mass Index, has limitations in accurately assessing body composition and health risks.
BMI, or Body Mass Index, has limitations in accurately assessing body composition and health risks.
Firstly, it fails to differentiate between muscle mass and fat mass, and does not consider the distribution of fat in the body.
This means that people with high muscle mass might be classified as overweight or obese, despite having a healthy level of body fat.
Conversely, individuals with a normal BMI may still have a high percentage of body fat if it is concentrated in the abdominal region, which is associated with increased health risks.
Additionally, BMI solely relies on height and weight measurements, ignoring the proportion of muscle mass, which can result in higher BMI readings for individuals with more muscle mass.
Furthermore, BMI does not account for individual variations in body composition and genetic factors, such as differences in bone density or fat distribution.
Consequently, two people with the same BMI can have different body compositions and varying health risks.
2. Inaccuracy in special populations
 BMI charts for children and adolescents, which consider age and sex-specific percentiles, may not provide an accurate assessment of their health or future health risks.
BMI charts for children and adolescents, which consider age and sex-specific percentiles, may not provide an accurate assessment of their health or future health risks.
BMI alone fails to account for changes in body composition during growth and development.
Athletes and individuals with high muscle mass often have a higher BMI, potentially leading to misclassification as overweight or obese. This overlooks their actual body fat percentage and overall health.
Moreover, older adults experience shifts in body composition, such as muscle loss and increased fat mass, which can result in an underestimation of health risks when relying solely on BMI.
3. Lack of consideration for overall health
 BMI (Body Mass Index) has limitations when it comes to assessing health.
BMI (Body Mass Index) has limitations when it comes to assessing health.
Firstly, it overlooks other vital health markers like blood pressure, cholesterol levels, blood sugar levels, and cardiovascular fitness, which provide a more comprehensive understanding of an individual’s health and disease risk.
Secondly, BMI fails to consider lifestyle factors such as diet, physical activity levels, and overall fitness, leading to different metabolic health profiles among individuals with the same BMI.
Lastly, BMI disregards the complexity of health conditions and disease risk factors as it cannot capture the influence of genetics, lifestyle, and body composition on conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease.
Reason 1: Body Composition Matters More
 Understanding body composition is crucial because it provides a more comprehensive picture of an individual’s overall health and fitness level beyond just body weight.
Understanding body composition is crucial because it provides a more comprehensive picture of an individual’s overall health and fitness level beyond just body weight.
Body composition refers to the proportion of fat, muscle, bone, and other tissues in the body.
Two people can have the same body weight but differ significantly in their body composition, which has implications for their health and well-being.
Exploring alternative methods to measure body composition:
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA)
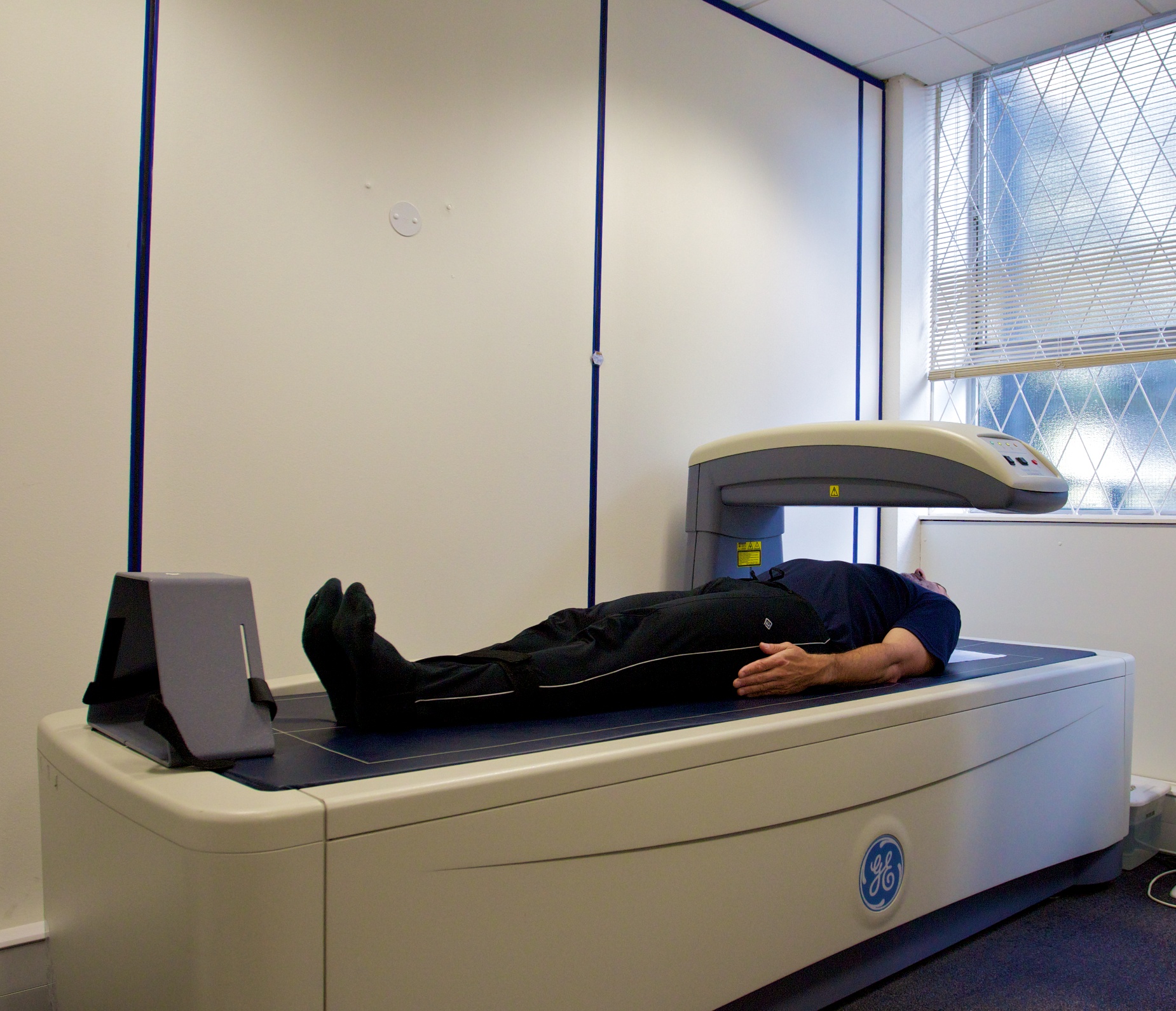 DEXA is a highly accurate method for measuring body composition.
DEXA is a highly accurate method for measuring body composition.
It uses X-rays to differentiate between fat, muscle, and bone mass.
DEXA scans provide detailed information about fat distribution, bone density, and muscle mass in various body regions.
Although it is considered the gold standard, DEXA scans are expensive and not easily accessible for routine assessments.
Bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA)
 BIA measures body composition by sending a low-level electrical current through the body and measuring the resistance encountered.
BIA measures body composition by sending a low-level electrical current through the body and measuring the resistance encountered.
This method estimates body fat percentage based on the principle that fat conducts less electricity than muscle.
BIA devices are portable and relatively inexpensive, making them more accessible.
However, BIA can be less accurate than DEXA and may be affected by factors such as hydration status and body temperature.
Skinfold thickness measurements
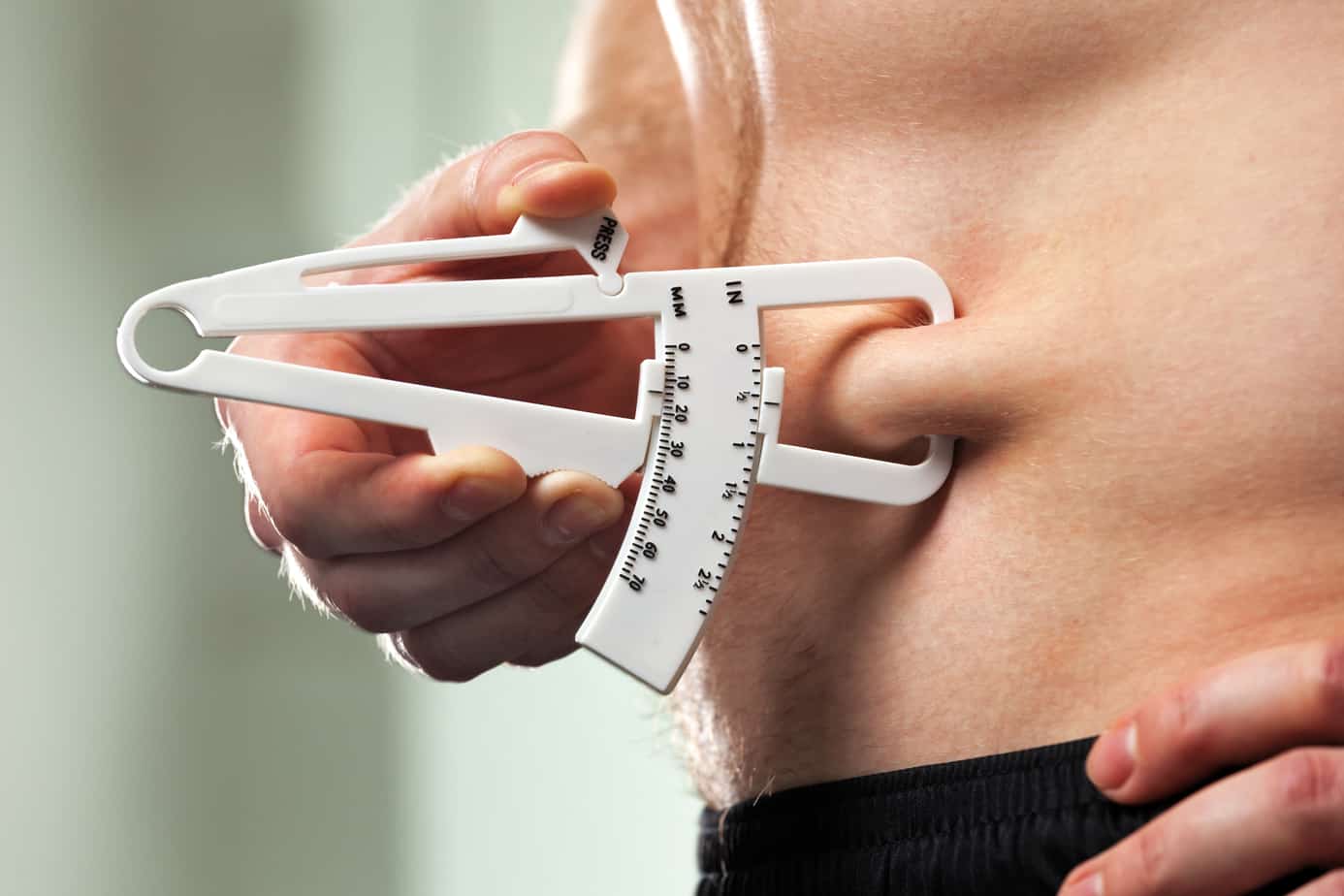 Skincare thickness measurements involve using calipers to pinch and measure the thickness of the skin and subcutaneous fat at specific sites on the body.
Skincare thickness measurements involve using calipers to pinch and measure the thickness of the skin and subcutaneous fat at specific sites on the body.
These measurements are then used to estimate overall body fat percentage.
Skinfold measurements are less expensive and accessible, but they require skilled operators to ensure accuracy.
Additionally, the accuracy of skinfold measurements can vary depending on the individual’s body type and the skill of the operator.
Reason 2: Muscle Mass and Fitness Levels
 BMI fails to consider the significance of muscle mass and its impact on overall health.
BMI fails to consider the significance of muscle mass and its impact on overall health.
Muscle mass plays a crucial role in metabolism, physical performance, and disease prevention.
Individuals with a higher muscle mass tend to have a better metabolic profile and a lower risk of chronic conditions.
Therefore, focusing solely on BMI can misclassify individuals with a higher muscle mass as overweight or obese, neglecting their actual level of fitness and health.
Reason 3: Personalization and Individual Differences
 Every individual is unique, and health assessment should reflect this individuality.
Every individual is unique, and health assessment should reflect this individuality.
Genetic factors influence body composition, metabolism, and disease risk, making personalized approaches to health management essential.
By acknowledging the variations between individuals, including their genetic predispositions, it is possible to tailor health strategies and interventions to suit their specific needs, rather than relying on a one-size-fits-all metric like BMI.
Conclusion
BMI, once considered a reliable indicator of weight status and health, has been proven to be an inaccurate and outdated metric.
Its limitations in accounting for body composition, muscle mass, and overall health make it inadequate for assessing individual well-being.
It is crucial to abandon the use of BMI as a sole measurement tool and instead embrace more comprehensive approaches that consider body composition, muscle mass, and personalized factors.
By doing so, we can promote a more accurate understanding of health and implement strategies that truly benefit individuals’ well-being.
It’s time to move beyond the limitations of BMI and embrace a more holistic and personalized approach to health assessment.
Are you tired of relying on outdated and inaccurate metrics like BMI to assess your health and fitness?
As we've uncovered the shortcomings of BMI and explained why it's time to move on to better, more comprehensive methods.
But that's not all – we want to introduce you to the revolutionary PrimaJust weight loss method.
PrimaJust is a cutting-edge approach to weight loss that takes into account your unique body composition, metabolism, and genetic factors.
It's a personalized and holistic method that goes beyond traditional weight loss strategies.
Download our still-free report today and discover The Exact Method to Unlock Your Metabolism for All-Natural Weight Loss using PrimaJust, enabling you to lose 1-3 pounds per week automatically—No Diet or Exercise Needed!
Don't miss this opportunity to transform your approach to health and wellness with PrimaJust.
Download now and start your journey toward a healthier, happier you!
[Source]Free Report
If you have any questions or comments, please leave them below.
Be inspired by these thought-provoking related blog posts
-
Unmasking Low Carb Diet: 8 Disturbing Reasons for Failure
Low-carb diets have gained immense popularity in recent years, promising rapid weight loss and improved…
-
Risks of Ozempic: 7 Reasons It's Dangerous for Weight Loss
In the pursuit of weight loss, people often seek various methods and medications to aid…
-
The Alarming Risk of Low Carb Diets Unveiled
Low carb diets have gained significant popularity in recent years, with many individuals turning to…